A rectangular beam is cut from a cylindrical log – A rectangular beam cut from a cylindrical log presents a fascinating study in geometry and engineering. This undertaking involves understanding the relationship between the log’s dimensions and the resulting beam’s properties, optimizing the beam’s dimensions for specific applications, and employing appropriate techniques for cutting and shaping the beam.
Delving into this topic unveils a wealth of knowledge and practical insights.
Geometric Properties of a Cylindrical Log
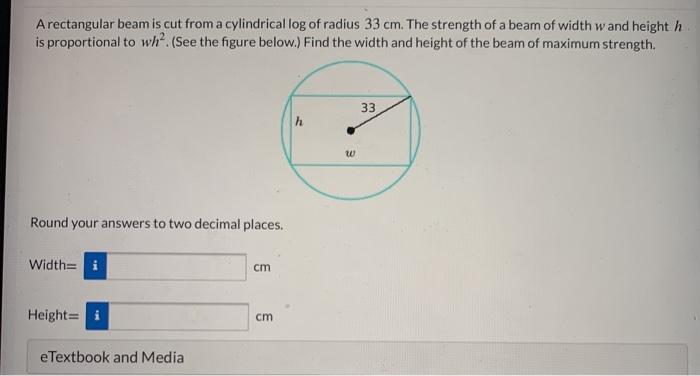
A cylindrical log is characterized by its circular cross-section and uniform diameter throughout its length. Understanding the geometric properties of a cylindrical log is essential for determining the optimal dimensions of a rectangular beam that can be cut from it.
Relationship between Radius and Diameter
The radius (r) of a cylindrical log is half of its diameter (d). The diameter represents the width of the log across its center, while the radius is the distance from the center to the edge.
Volume of a Cylindrical Log
The volume (V) of a cylindrical log can be calculated using the formula:
V = πr²h
where:
- π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the radius of the log
- h is the length of the log
Impact of Log Length on Volume, A rectangular beam is cut from a cylindrical log
The length of the log directly affects its volume. As the length increases, so does the volume, assuming the radius remains constant.
Rectangular Beam Dimensions: A Rectangular Beam Is Cut From A Cylindrical Log
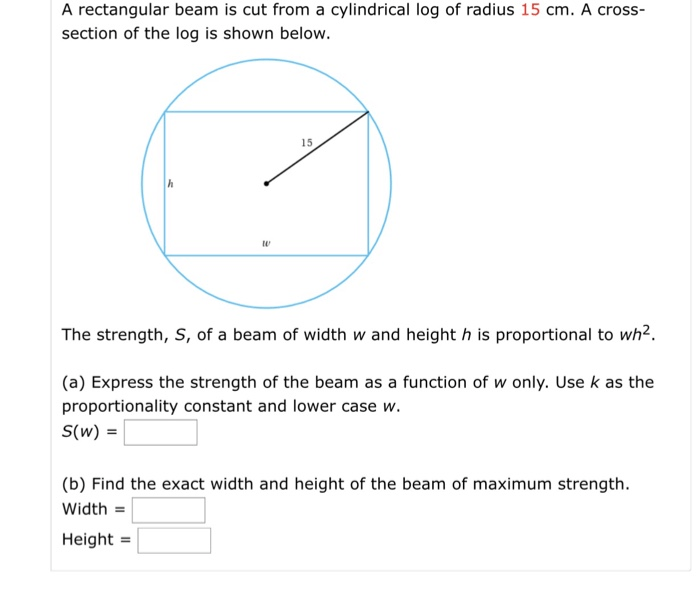
To determine the optimal dimensions of a rectangular beam that can be cut from a cylindrical log, it is necessary to maximize the beam’s cross-sectional area.
Maximizing Cross-Sectional Area
The cross-sectional area (A) of a rectangular beam is given by:
A = width × height
To maximize the cross-sectional area, it is necessary to find the combination of width and height that produces the largest value.
Trade-offs between Beam Width and Height
The width and height of the beam are interdependent. Increasing the width will decrease the height, and vice versa. Therefore, it is important to consider the trade-offs between these dimensions based on the specific application.
Cutting and Shaping the Beam
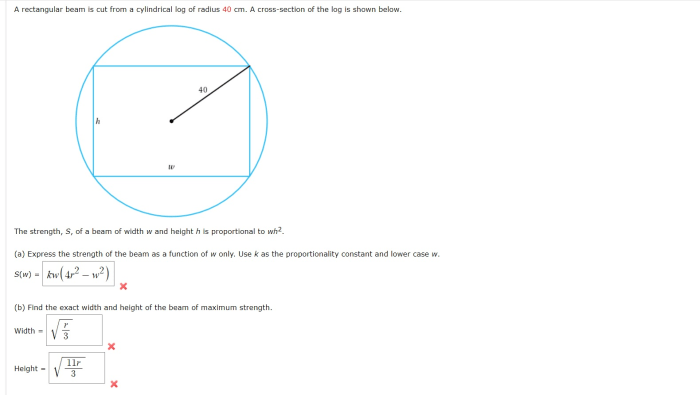
Cutting a rectangular beam from a cylindrical log involves several steps.
Cutting Process
The log is first cut into two halves along its length. The flat surfaces of the halves are then used as the top and bottom of the beam. The sides of the beam are cut using a saw or other appropriate tool.
Tools and Techniques
Proper tools and techniques are essential for safe and efficient cutting. A chainsaw or circular saw can be used for cutting the log, while a handsaw or miter saw can be used for shaping the beam.
Safety Precautions
Safety precautions should be taken during the cutting process. Wear appropriate protective gear, including safety glasses, gloves, and earplugs. Ensure the log is securely supported and stable before cutting.
Applications of Rectangular Beams
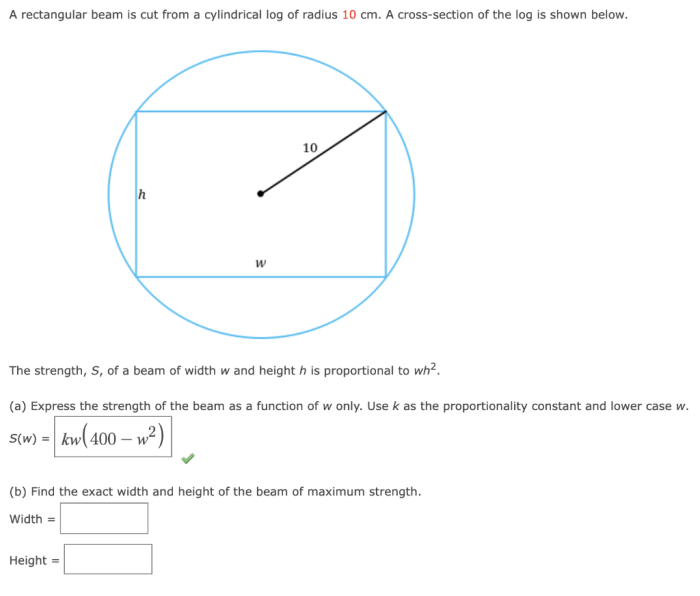
Rectangular beams are widely used in various applications due to their strength, durability, and versatility.
Construction
Rectangular beams are commonly used in construction for framing, joists, and headers. They provide structural support for walls, roofs, and floors.
Engineering
In engineering, rectangular beams are used in bridges, machinery, and other structures. They can withstand high loads and are suitable for applications requiring strength and rigidity.
Examples
Examples of structures or products that utilize rectangular beams include:
- Building frames
- Bridges
- Furniture
- Machinery frames
Questions Often Asked
What is the relationship between the radius and diameter of a cylindrical log?
The diameter of a cylindrical log is twice its radius.
How is the volume of a cylindrical log calculated?
The volume of a cylindrical log is given by the formula: V = πr²h, where r is the radius and h is the height of the log.
What factors influence the optimal dimensions of a rectangular beam cut from a cylindrical log?
The optimal dimensions of a rectangular beam cut from a cylindrical log depend on the desired cross-sectional area and the strength requirements of the application.