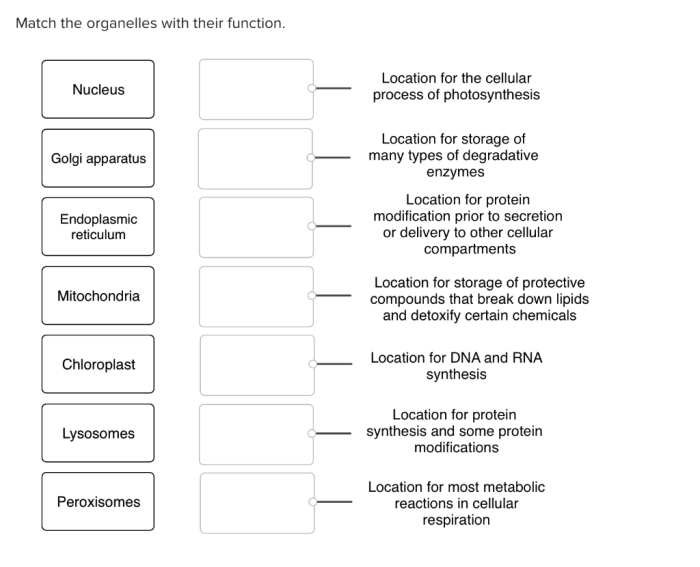
Match the organelle with its function. embarks on an intellectual odyssey, delving into the intricate world of organelles, the microscopic marvels that orchestrate the symphony of cellular life. From the nucleus, the control center of the cell, to the mitochondria, the energy powerhouses, organelles play a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of our bodies.
Throughout this discourse, we will unravel the functions of various organelles, exploring how they contribute to the overall health and well-being of cells. We will also delve into the fascinating realm of organelle evolution, tracing their adaptation over time to perform specialized tasks.
By understanding the intricate workings of organelles, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and resilience of life at the cellular level.
Organelle Identification
Organelles are specialized compartments within cells that perform specific functions essential for cell survival and function. Each organelle has a unique structure and composition that enables it to carry out its specific tasks.
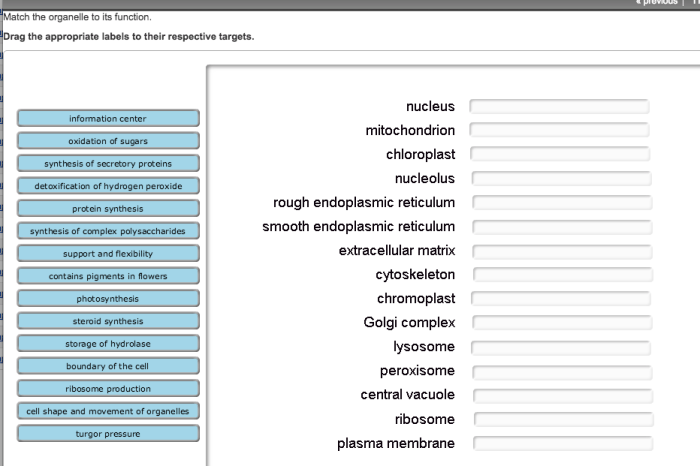
Common organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and ribosomes. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material, mitochondria produce energy, the endoplasmic reticulum processes proteins and lipids, the Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins, lysosomes digest cellular waste, and ribosomes synthesize proteins.
Organelle Functions
Organelles play crucial roles in maintaining cell homeostasis and ensuring proper cell function. The nucleus controls cell growth and division, mitochondria provide energy for cellular processes, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus process and modify proteins and lipids, lysosomes digest cellular waste, and ribosomes synthesize proteins.
The coordinated function of organelles is essential for overall cell health. For example, proteins synthesized by ribosomes are processed by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus before being transported to their final destinations within the cell.
Organelle Interactions: Match The Organelle With Its Function.
Organelles do not operate in isolation but rather interact and communicate with each other to maintain cell homeostasis. For instance, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus work together to process and modify proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes proteins, while the Golgi apparatus modifies and packages them for secretion or intracellular use.
Organelles also communicate through signaling molecules and physical interactions. For example, calcium ions released from the endoplasmic reticulum can trigger changes in mitochondrial activity.
Organelle Evolution

Organelles have evolved over time to perform specialized functions. Mitochondria, for example, are believed to have originated from symbiotic bacteria that were engulfed by eukaryotic cells. Over time, these bacteria lost their ability to live independently and became integrated into the cell as an organelle responsible for energy production.
The evolution of organelles has allowed cells to become more complex and efficient in carrying out their functions.
Organelle Dysfunction

Organelle dysfunction can have severe consequences for cell health and function. For example, mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to reduced energy production, which can impair cell growth and division. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction can disrupt protein synthesis and folding, leading to the accumulation of misfolded proteins and cell death.
Organelle dysfunction can contribute to the development of various diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer.
Organelle Imaging
Visualizing organelles is essential for studying their structure and function. Microscopy techniques, such as fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy, allow researchers to observe organelles in living and fixed cells.
Microscopy techniques have provided valuable insights into organelle dynamics, interactions, and their role in cellular processes.
Organelle Engineering
Organelle engineering involves modifying organelles to improve cell function or treat diseases. For example, researchers have engineered mitochondria to increase energy production or deliver therapeutic molecules to specific cells.
Organelle engineering has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of various diseases by targeting specific organelles and modulating their function.
Organelle Comparisons
| Organelle | Location | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Center of the cell | Double membrane with nuclear pores | Contains genetic material and controls cell growth and division |
| Mitochondria | Throughout the cell | Double membrane with cristae | Produces energy for cellular processes |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Throughout the cell | Network of membranes | Processes and modifies proteins and lipids |
| Golgi Apparatus | Near the nucleus | Stack of flattened membranes | Modifies and packages proteins |
| Lysosomes | Throughout the cell | Single membrane with hydrolytic enzymes | Digests cellular waste |
| Ribosomes | Free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum | Small, granular structures | Synthesizes proteins |
Question Bank
What is the primary function of the nucleus?
The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material and controls cellular activities.
How do mitochondria contribute to cellular energy production?
Mitochondria generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in protein synthesis?
The endoplasmic reticulum folds, modifies, and transports proteins.
