Lean supply chain management focuses on eliminating waste: sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with authoritative academic style and brimming with originality from the outset. By delving into the intricacies of lean supply chain management, we embark on a journey of discovery, uncovering the secrets of optimizing value streams, fostering collaboration, and harnessing technology to achieve unparalleled efficiency.
Throughout this discourse, we will explore the core principles and objectives of lean supply chain management, examining how it has transformed industries and empowered businesses to reach new heights of productivity. We will identify the different types of waste commonly found in supply chains and discuss the methods and techniques used to eliminate them, emphasizing the importance of continuous improvement in waste reduction.
1. Defining Lean Supply Chain Management
Lean supply chain management (LSCM) is a systematic approach that focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It emphasizes the principles of value creation, continuous improvement, and collaboration.
Key principles of LSCM include:
- Customer focus: Understanding and meeting customer needs
- Waste elimination: Identifying and removing non-value-added activities
- Continuous improvement: Striving for ongoing enhancements in processes
- Collaboration: Fostering cooperation among supply chain partners
Examples of successful LSCM implementations include Toyota’s production system, Dell’s direct-to-customer model, and Amazon’s e-commerce platform.
2. Identifying and Eliminating Waste: Lean Supply Chain Management Focuses On Eliminating Waste:
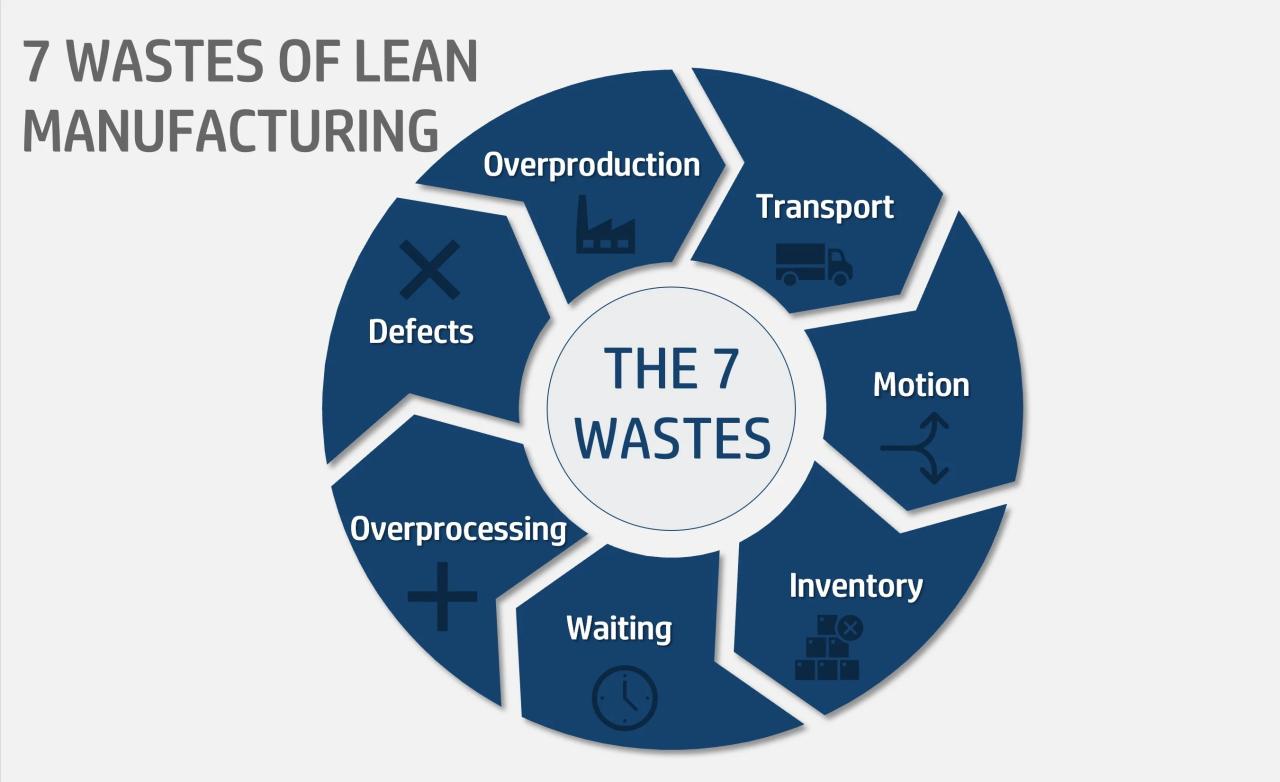
Waste in supply chains can take various forms, including:
- Overproduction
- Waiting
- Transportation
- Inventory
- Defects
Methods for identifying and eliminating waste include:
- Value stream mapping
- Root cause analysis
- Lean tools (e.g., 5S, kaizen)
Continuous improvement is crucial for sustained waste reduction.
3. Optimizing Value Stream
Value stream mapping is a technique used to visualize and analyze the flow of materials and information through a supply chain.
Steps for creating and analyzing value stream maps include:
- Identify the value stream
- Map the current state
- Identify waste
- Design a future state
Value stream mapping helps identify and eliminate waste by providing a comprehensive view of the supply chain.
4. Collaboration and Information Sharing
Collaboration and information sharing are essential for effective LSCM.
Methods and tools for collaboration and information sharing include:
- Supplier relationship management (SRM)
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
- Electronic data interchange (EDI)
Successful collaboration initiatives in supply chain management include the Toyota Supplier Network and the Voluntary Interindustry Commerce Solutions (VICS) Association.
5. Technology and Lean Supply Chain Management
Technology plays a vital role in supporting LSCM.
Technologies such as:
- ERP systems
- Radio frequency identification (RFID)
- Data analytics
can improve efficiency and reduce waste by providing real-time visibility, automating processes, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
Examples of innovative technology solutions used in LSCM include Amazon’s robotic fulfillment centers and Walmart’s RFID-enabled inventory management system.
6. Measuring and Evaluating Performance
Measuring and evaluating performance is crucial for continuous improvement in LSCM.
Key metrics and indicators used to assess performance include:
- Customer satisfaction
- Inventory turnover
- Lead time
- Cost
Best practices for performance measurement and evaluation include:
- Establishing clear performance goals
- Collecting and analyzing data regularly
- Using performance metrics to drive decision-making
7. Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing LSCM poses challenges, including:
- Resistance to change
- Lack of collaboration
- Technology adoption
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include:
- Building a strong business case
- Engaging stakeholders
- Investing in training and development
LSCM offers significant opportunities for businesses, including:
- Improved customer service
- Reduced costs
- Increased efficiency
FAQ
What are the key principles of lean supply chain management?
The key principles of lean supply chain management include: identifying and eliminating waste, optimizing value streams, fostering collaboration and information sharing, and leveraging technology to improve efficiency.
How does lean supply chain management help businesses?
Lean supply chain management helps businesses reduce costs, improve customer service, increase flexibility, and gain a competitive advantage.
What are the challenges of implementing lean supply chain management?
The challenges of implementing lean supply chain management include: changing organizational culture, overcoming resistance to change, and integrating lean principles with existing systems and processes.