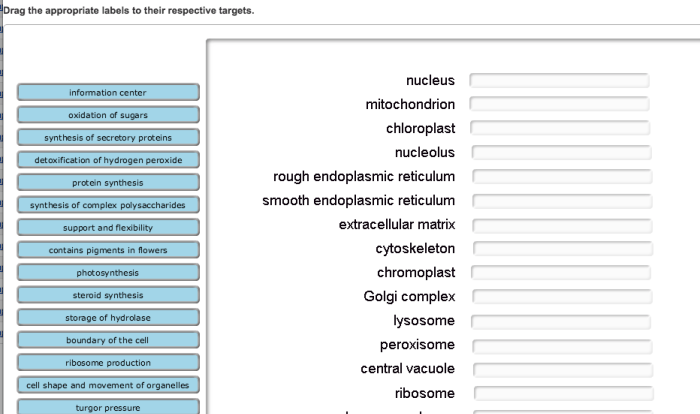
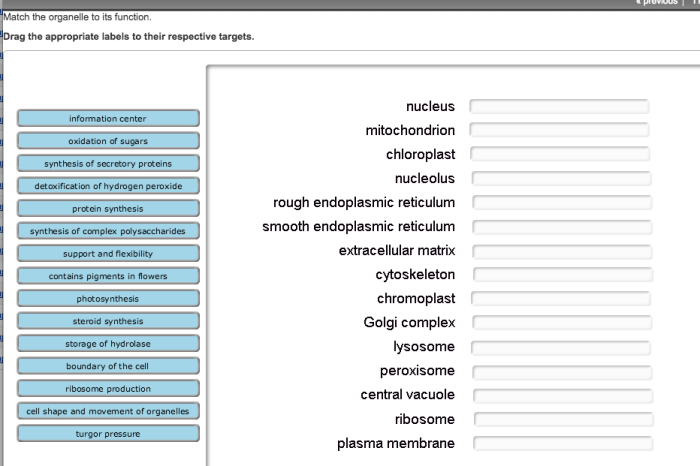
Match the organelle to its function – In the intricate realm of biology, the harmonious interplay of organelles within cells governs their very essence. This exploration into matching organelles to their functions unveils the profound relationship between their structure and purpose, revealing the remarkable symphony that sustains life.
Delving into the depths of eukaryotic cells, we encounter a myriad of organelles, each fulfilling a specific role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and executing vital processes. From the powerhouses of mitochondria to the protein synthesis hubs of ribosomes, each organelle is a testament to the intricate design of life.
Organelle Functions Table
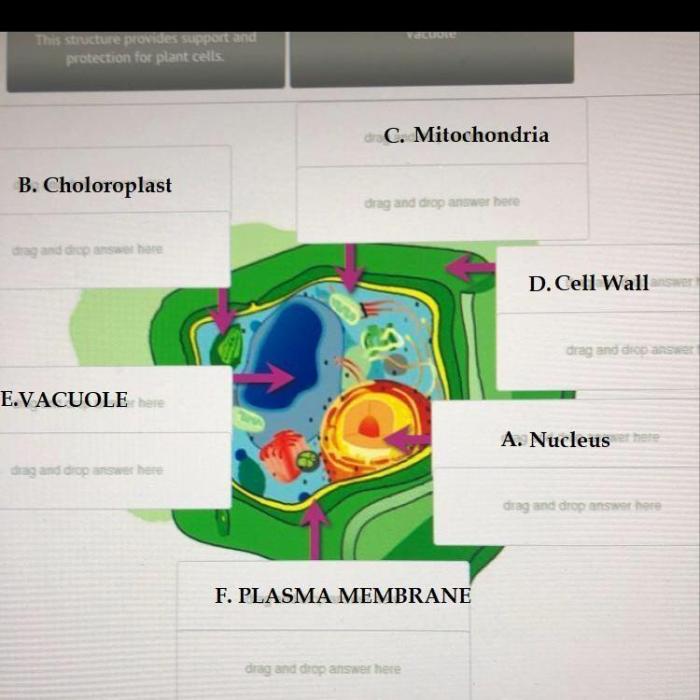
Creating an HTML table is a structured and organized way to display the functions of organelles. It allows for easy comparison and reference of information.
Here’s an example of an HTML table with four responsive columns:
| Organelle | Function | Location | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitochondria | Energy production | Cytoplasm | Double membrane |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis | Plant cells | Double membrane |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | Cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum | Small and large subunits |
| Golgi apparatus | Protein modification and packaging | Cytoplasm | Flattened sacs |
Matching Organelles to Functions: Match The Organelle To Its Function
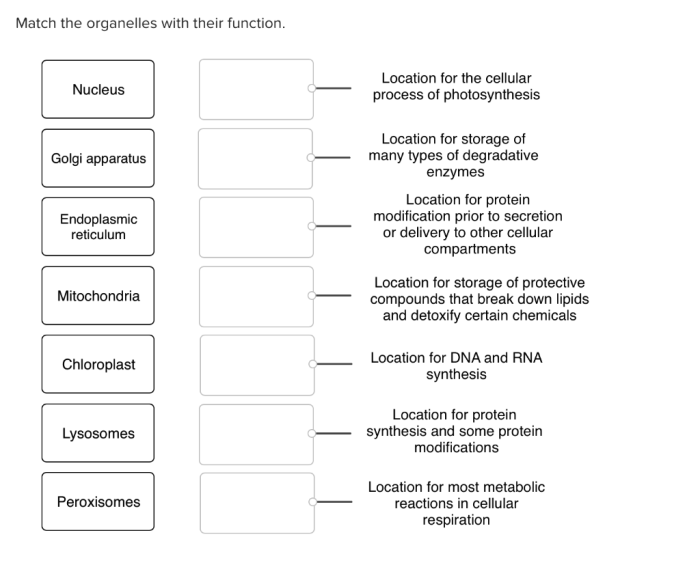
Eukaryotic cells are complex and contain a variety of organelles that perform specific functions essential for cell survival and operation. Understanding the functions of these organelles is crucial for comprehending cellular biology.
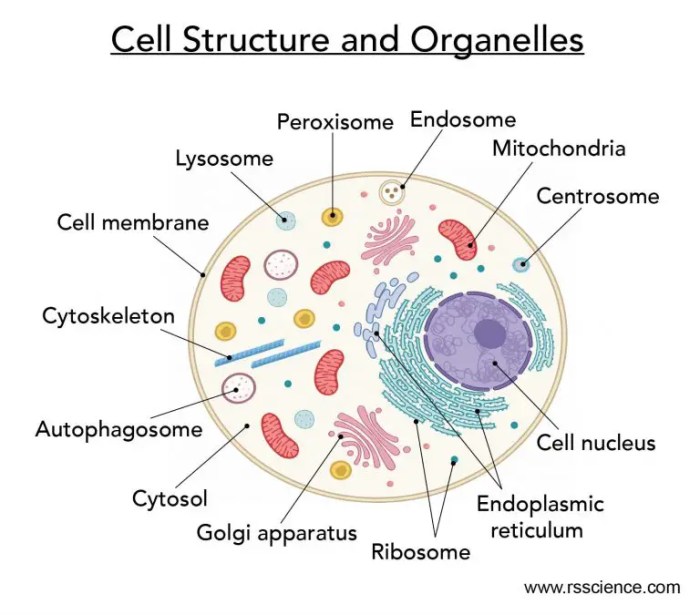
Common Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
The following list presents some common organelles found in eukaryotic cells, along with their primary functions and locations within the cell:
- Nucleus:The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). It is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and contains nucleoli, which are responsible for ribosome production.
- Ribosomes:Ribosomes are small, dense organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
They can be found either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):The ER is a network of membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification. The rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface, while the smooth ER does not.
- Golgi Apparatus:The Golgi apparatus is a complex of flattened sacs that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or storage. It is located near the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Lysosomes:Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They break down and recycle cellular waste, including damaged organelles and foreign materials.
- Mitochondria:Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouses of the cell” because they produce most of the cell’s energy through cellular respiration. They are found throughout the cytoplasm.
- Chloroplasts (in plant cells):Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Vacuoles:Vacuoles are membrane-bound compartments that store substances such as water, salts, and waste products. They are found in both plant and animal cells but are particularly large in plant cells.
- Peroxisomes:Peroxisomes are small, membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes that break down toxic substances and produce hydrogen peroxide.
- Centrosomes:Centrosomes are organelles that organize microtubules and are involved in cell division. They are located near the nucleus.
Organelle Structure and Function Relationships
Organelles, the specialized compartments within cells, exhibit a remarkable correlation between their structure and function. The unique shape and composition of each organelle enable it to perform its specific role efficiently.
Shape and Function, Match the organelle to its function
The shape of an organelle often reflects its function. For instance, the flattened sacs of the Golgi apparatus provide a large surface area for protein modification and sorting. The elongated shape of mitochondria, with numerous folds (cristae), increases the surface area for ATP production.
Composition and Function
The composition of an organelle also contributes to its function. The ribosomes, responsible for protein synthesis, are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. The presence of rRNA in ribosomes enables them to bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) and facilitate protein assembly.
Examples
- Lysosomes:Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes. Their spherical shape allows them to fuse with other organelles or endocytosed material, enabling the breakdown of ingested substances.
- Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts are photosynthetic organelles found in plant cells. Their flattened, disc-like shape maximizes the surface area for capturing sunlight, facilitating the process of photosynthesis.
Interactive Organelle Function Quiz
Test your knowledge of organelle functions with our interactive quiz. This quiz will help you solidify your understanding of the roles of different organelles in cell biology.
Quiz Questions
- Which organelle is responsible for protein synthesis?
- What is the function of the mitochondria?
- Which organelle is involved in the transport of materials within the cell?
- What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
- Which organelle contains the cell’s genetic material?
Answer Key:
- Ribosomes
- Energy production
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Protein modification and packaging
- Nucleus
Feedback for incorrect answers:
- The nucleus is responsible for storing the cell’s genetic material, not protein synthesis.
- Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, not energy production in animal cells.
- Lysosomes are involved in digestion, not the transport of materials within the cell.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis and transport, not protein modification and packaging.
- Mitochondria are responsible for energy production, not storing the cell’s genetic material.
Visual Representation of Organelle Functions

Creating a visual representation of organelle functions can enhance understanding and retention of complex biological processes. Infographics and flowcharts are effective tools for visualizing these functions, providing a clear and concise overview of the roles of different organelles within the cell.
These visual representations should utilize clear and concise language to explain the functions of each organelle, avoiding jargon or overly technical terms. Visually appealing elements, such as color-coding, shapes, and icons, can make the infographic more engaging and easier to understand.
Interactive elements, like clickable links to additional information or animations, can further enhance the learning experience.
Flowchart Representation
A flowchart is a graphical representation that uses shapes and arrows to illustrate the flow of information or processes. In the context of organelle functions, a flowchart can be used to show the relationship between different organelles and their specific roles within the cell.
Arrows can be used to indicate the direction of flow of molecules or information between organelles.
Infographic Representation
An infographic is a visually appealing representation of information that combines text, images, and data. In the context of organelle functions, an infographic can be used to provide a comprehensive overview of the different organelles and their functions. It can include images of organelles, their structures, and their locations within the cell.
The infographic can also include charts and graphs to illustrate the relative importance or abundance of different organelles within the cell.
Query Resolution
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating ATP through cellular respiration.
Where are ribosomes located within the cell?
Ribosomes can be found either freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, where they engage in protein synthesis.
How does the structure of the Golgi apparatus contribute to its function?
The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened sacs called cisternae, which provide a large surface area for the modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins.