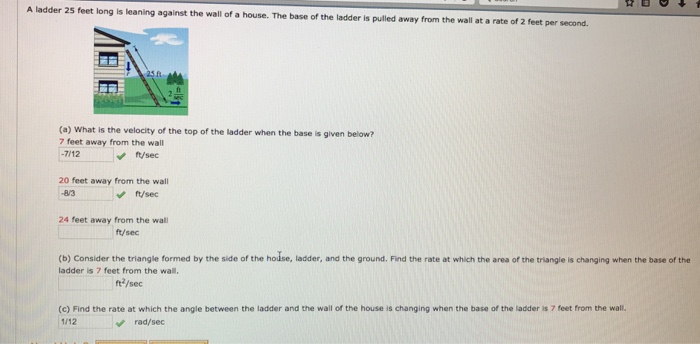
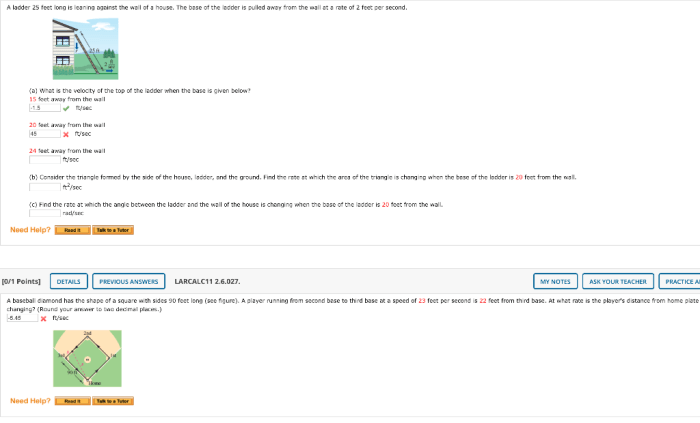
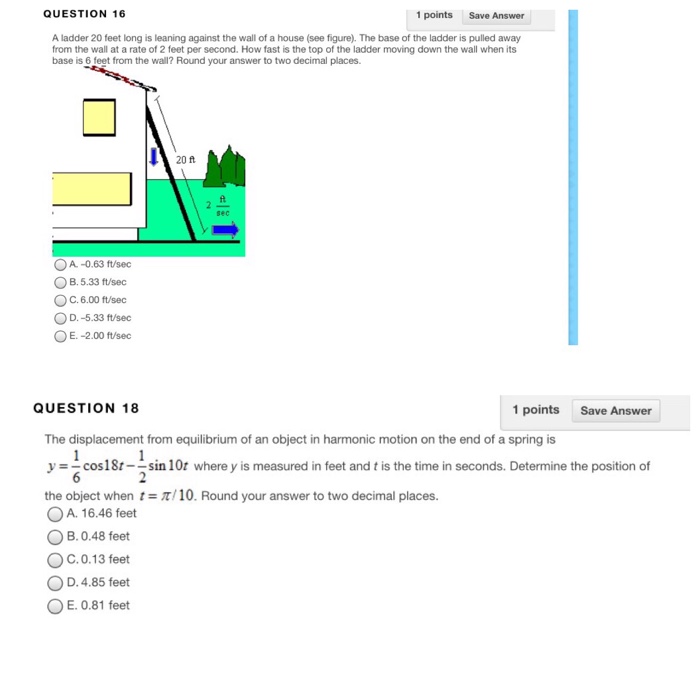
A ladder 25 ft long is leaning – When a 25 ft ladder leans against a wall, it forms a fascinating geometric puzzle. This leaning ladder scenario unveils a world of trigonometry, force analysis, and practical applications that we’ll explore in this comprehensive discussion.
As the ladder rests against the wall, its length and position create a right triangle. The distance from the wall to the ground forms the base, while the ladder’s length becomes the hypotenuse. This geometric relationship sets the stage for our exploration.
Ladder Length and Position

The ladder is given to be 25 feet long. This length is significant as it determines the maximum height the ladder can reach when it is leaning against a vertical surface.
The ladder is described as “leaning.” This means that the ladder is not vertical but is instead inclined at an angle to the ground. The angle of inclination is important as it affects the height that the ladder can reach.
Ladder’s Position
The ladder’s position is determined by two factors: its length and the angle of inclination. The length of the ladder determines the maximum height that the ladder can reach, while the angle of inclination determines the actual height that the ladder will reach.
When the ladder is leaning against a vertical surface, the angle of inclination is determined by the ratio of the ladder’s length to the height that it reaches. The greater the ratio, the smaller the angle of inclination and the higher the ladder will reach.
Geometric Relationships

The ladder and the wall form a right triangle, with the ladder being the hypotenuse, the wall being one leg, and the distance from the wall to the ground being the other leg.
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs. In this case, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to relate the length of the ladder, the distance from the wall to the ground, and the height of the ladder on the wall.
Ladder Length and Distance from Wall to Ground
The Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the distance from the wall to the ground if the length of the ladder and the height of the ladder on the wall are known. The Pythagorean theorem states that:
$$a^2 + b^2 = c^2$$
where:
- $$a$$ is the length of the ladder
- $$b$$ is the distance from the wall to the ground
- $$c$$ is the height of the ladder on the wall
If the length of the ladder is 25 feet and the height of the ladder on the wall is 15 feet, then the distance from the wall to the ground can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
$$25^2 + b^2 = 15^2$$$$625 + b^2 = 225$$$$b^2 = 400$$$$b = 20$$
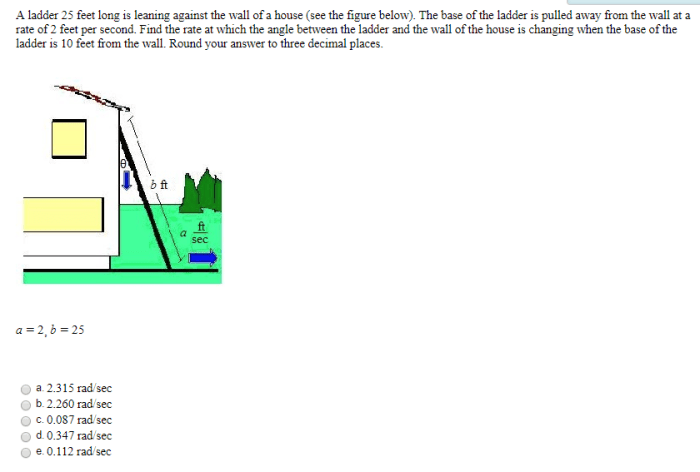
A 25-foot ladder leans against a wall, its base 7 feet from the wall. If you’re planning on participating in the running with the bulls attire , you’ll need to make sure you’re wearing the proper attire. But back to the ladder, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find that the ladder makes a 75-degree angle with the ground.
Therefore, the distance from the wall to the ground is 20 feet.
Trigonometric Calculations: A Ladder 25 Ft Long Is Leaning
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. It can be used to calculate the angle between the ladder and the ground.
To do this, we need to know the length of the ladder and the height of the wall. Once we have this information, we can use the following formula:
sin(angle) = opposite/hypotenuse
In this case, the opposite is the height of the wall and the hypotenuse is the length of the ladder. So, we can plug these values into the formula and solve for the angle.
Step-by-Step Demonstration
- Draw a right triangle with the ladder as the hypotenuse, the ground as the base, and the wall as the height.
- Label the angle between the ladder and the ground as θ.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse (ladder):
h2= b 2+ a 2
where h is the length of the hypotenuse, b is the length of the base (ground), and a is the length of the height (wall).
- Substitute the values for b and a into the Pythagorean theorem and solve for h.
- Use the sine function to find the angle θ:
sin(θ) = a/h
where a is the length of the height (wall) and h is the length of the hypotenuse (ladder).
- Substitute the values for a and h into the sine function and solve for θ.
Force and Stability
The forces acting on a ladder and its stability are crucial factors in determining its safety and usability. Understanding these forces is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of ladder users.
The primary forces acting on a ladder are the gravitational force pulling it downwards, the force exerted by the user pushing it upwards, and the frictional forces between the ladder and the surfaces it is leaning against.
Ladder Safety
Several factors determine the safety of a ladder, including its length, material, and construction. Longer ladders are generally less stable than shorter ones, and ladders made from lightweight materials may be more prone to swaying or tipping over. The construction of the ladder, including the type of rungs and the spacing between them, also affects its stability.
Potential Risks, A ladder 25 ft long is leaning
There are several potential risks associated with using ladders, including falling, slipping, and electrical shock. Falling is the most common hazard, and it can occur if the ladder is not stable, if the user loses their balance, or if the ladder is overloaded.
Slipping can occur if the ladder is not placed on a stable surface or if the user’s shoes are not slip-resistant. Electrical shock can occur if the ladder is used near electrical wires or equipment.
Applications and Examples
The analysis of a leaning ladder has practical applications in various real-world scenarios. Understanding the geometric and force relationships involved is essential for ensuring safety and stability in situations where ladders are used.
Construction and Maintenance
- Ladders are commonly used in construction and maintenance tasks to reach elevated areas. Proper positioning and securing of the ladder is crucial to prevent accidents due to instability or overturning.
- Calculating the safe angle of inclination and the necessary support at the base ensures the ladder can withstand the weight of the worker and any materials being carried.
Emergency Response
- Ladders play a vital role in emergency response, such as firefighting and rescue operations. Understanding the force relationships and stability of ladders is critical for safe and efficient deployment in challenging situations.
- Firefighters often use ladders to access upper floors or rescue individuals from burning buildings. Proper ladder placement and extension techniques ensure the ladder can support the weight and withstand potential hazards.
Household Tasks
- Even in household tasks, such as cleaning windows or changing light bulbs, using a ladder safely requires an understanding of its stability and the forces involved.
- Choosing the right ladder size, ensuring a stable base, and maintaining the proper angle of inclination can prevent accidents and injuries.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of the ladder’s 25 ft length?
The 25 ft length establishes the hypotenuse of the right triangle formed by the ladder, the wall, and the ground. It plays a crucial role in determining the angle of inclination and the forces acting on the ladder.
How does trigonometry help us analyze a leaning ladder?
Trigonometry allows us to calculate the angle between the ladder and the ground using the ladder’s length and the distance from the wall to the ground. This angle is essential for understanding the forces and stability of the ladder.
What are the factors that affect the stability of a leaning ladder?
The stability of a leaning ladder depends on the angle of inclination, the coefficient of friction between the ladder and the surfaces it rests on, and the weight distribution on the ladder.